XTRAN Example — Normalize Vocabulary in DSV Data
Scenario — you are receiving delimiter-separated value (DSV) data from various sources, and each source has its own vocabulary. You need to normalize terms across those multiple data sources.
XTRAN to the rescue!
The following example uses an XTRAN rules file comprising 124 non-comment lines of "meta-code" (XTRAN's rules language) to process delimiter-separated value data and normalize vocabulary in it, substituting preferred terms for synonyms.
The rules took one hour to write and ½ hour to debug. (That's right, only 1½ hours total!)
You can specify a preferred term for each DSV field, along with a set of synonyms for it. The rules will then, for each specified DSV field, change all synonyms to the preferred term and write out the results.
You specify preferred terms and synonyms for them, for each
DSV field that has them, via a "synonyms" file, in the
following format. Empty lines and lines starting with ; are
ignored.
<dsvfld>,<prftrm>,<syntrm>[[,...]]
where:
<dsvfld> |
is the DSV field number, 1-n, to be processed | |
<prftrm> |
is the preferred term for that field | |
<syntrm> |
are one or more synonyms for <prftrm> |
Note that the rules automatically accommodate DSV data with missing fields.
Here is an English paraphrase of the XTRAN rules:
Open synonym specifications file read-only
For each input line
Parse specification, store in data base
Close synonym specifications file
Open input DSV data file read-only
Create output file
For each DSV data input line
Initialize output line to empty
For each of input line's DSV fields
If field value is synonym for preferred term (direct DB lookup)
Add preferred term to output line
Else
Add field value to output line
Write output line
Close input and output files
How can such powerful and generalized data processing be automated in only 1½ hours and 124 lines of rules? Because there is so much capability already available as part of XTRAN's rules language. These rules take advantage of the following functionality:
- Text file input and output
- Text manipulation
- Delimited list manipulation
- Regular expression matching
- Environment variable manipulation
- Content-addressable data bases
The input to and output from XTRAN are untouched.
Process Flowchart
Here is a flowchart for this process, in which the elements are color coded:
- BLUE for XTRAN versions (runnable programs)
- ORANGE for XTRAN rules (text files)
- PURPLE for text data files
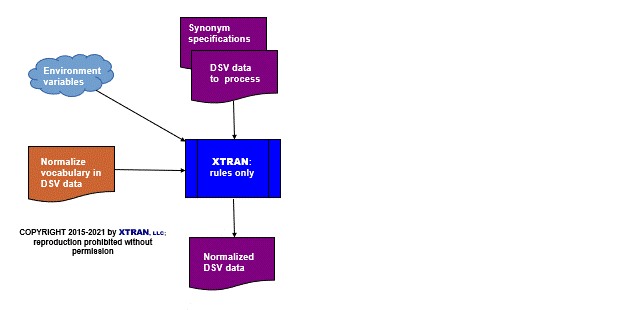
Input to XTRAN — synonym specifications:
3,country,location,venue 5,age,years
Input to XTRAN — DSV data to process:
Jones,Arthur,location,USA,years,25 Murgatroyd,Gertrude,venue,France,age,40 Baldwin,Agnes,location,USA Smith,Fred,country,Germany,years,19
Output from XTRAN — normalized DSV data:
Jones,Arthur,country,USA,age,25 Murgatroyd,Gertrude,country,France,age,40 Baldwin,Agnes,country,USA Smith,Fred,country,Germany,age,19